FAQ for Agent Coach text normalization
These frequently asked questions (FAQs) describe the impact of AI on text normalization in Agent Coach.
What is Agent Coach text normalization?
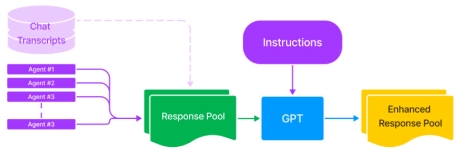
Agent Coach is a retrieval recommendation system that suggests relevant replies based on the chat history. Agents retrieve these replies from a response pool, which is a list of pre-set responses created during model training. The response pool consists of utterances gathered from chat transcripts that are frequently used by agents (for example, more than 10 to 100 times, depending on the volume). Despite using a model to fix such errors, these utterances are often riddled with typos and grammatical errors. Instead, administrators use a large language model (such as GPT) to correct typos and grammatical errors in all utterances included in the response pool.
For example,
-
Original utterance: tank you!
-
Enhanced utterance: Thank you!
Note: Administrators are not rewriting the utterance; the task is to fix typos and grammatical errors only.
What are the capabilities of Agent Coach text normalization?
Agent Coach performs text normalization edits on utterances to ensure grammatical correctness while preserving their intended meaning.
The figure below displays the enhanced response pool using GPT.
What is the intended use of Agent Coach text normalization?
Although Agent Coach text normalization has many valid uses cases, in the context of Nuance Digital Engagement Platform (NDEP) it uses GPT to provide grammatically correct responses to customers.
Intended use:
Agent Coach utilizes generative AI to suggest grammatically error-free responses for customer service agents.
Description:
Administrators initiate model training that the Agent Coach Engineering team completes. The training involves various pre-processing steps, such as:
-
Text normalization: Using GPT to correct typos and grammatical errors in the Agent Coach response pool.
-
Administrator review and approval: Once the normalization and training are complete, administrators review and approve the GPT-normalized response pool to finalize the curation process.
-
Agent Coach suggested GPT-normalized responses: Agent Coach then suggests GPT-normalized responses to customer service agents based on the chat context.
Finally, agents can choose to send these utterances as they are to consumers, edit them to better fit the context, or ignore them and provide their own response.
How was Agent Coach text normalization evaluated? What metrics are used to measure performance?
Agent Coach text normalization is a task where variations in text transform into a standardized format using generative AI. The text normalization evaluation metrics may vary based on the capabilities and the dataset used.
Here are a few capabilities of the Agent Coach text normalization:
-
Fix typos
-
Preserve original meaning
| Capability | Evaluation metric |
|---|---|
| Fix typos | Evaluating the correction of typos is not possible, as there is currently no metric available other than manual validation, which has already been conducted. |
| Preserve original meaning |
Users build a test dataset that serves as a reference for validating any alterations in meaning introduced by GPT. The results are highly favorable, achieving a 99 percent accuracy rate. Here is an example:
Users present the following question to GPT: Does the original utterance have the same meaning as the enhanced utterance? GPT responds with a yes or no. Users conduct this assessment on 100 utterances, achieving a 99% accuracy rate from GPT. Additionally, users perform manual validation on both the original and enhanced utterances. |
What are the limitations of Agent Coach text normalization? How can users minimize the impact of these limitations when using the system?
Under Agent Coach, when correcting typos and grammatical errors in utterances, GPT may unintentionally introduce modifications or additions that impact the meaning. This issue is observed in utterances consisting of just a few words. It does not result in a complete loss of meaning, but rather a reduction in generalization. Since GPT does not consider context as input, it may make subtle changes to the utterance text and its intended meaning. For example, the phrase 'Registered Email Address' might be replaced with 'Please provide your registered email address'. This has the potential to create confusion, particularly when the original utterance was used in a specific context where the updated version does not align with the expected response. For example, a customer asking for information to validate their identity might receive the response 'Registered Email Address' instead of 'Please provide your registered email address'.
Here is the table that describes potential limitations and preliminary mitigations of Agent Coach text normalization:
| Limitation | Corresponding goal from the Responsible AI standard | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
|
Risk of ungrounded content: GPT may alter the intended meaning of the utterance while attempting to correct typos or grammatical errors. Note: This risk is primarily observed in cases where the utterance consists of few words. It does not result in a complete loss of meaning but rather in a reduction in generalization. |
Failures and solutions |
To evaluate the prompt against the limitation, you can use GPT to evaluate the preservation of the intended meaning in both the original and enhanced utterances. You can provide GPT with examples of utterances that have undergone changes in meaning (such as, failures) and instruct it to use them as related examples to assess the robustness of text normalization. This establishes a benchmark for how often such changes occur, enabling the administrators to focus on reviewing only those utterances flagged by GPT as potentially losing meaning or generalization. Additionally, if an utterance is flagged in production, an administrator reviews it. There are three options available:
In any case, you can use the labeled dataset to evaluate and tune the prompt for ungrounded content. |
| Harmful content: GPT may not filter out responses that include harmful content. | Reliability and safety |
In production: If an utterance is flagged, the administrator reviews it. There are three options available:
Red teaming exercise: In addition to existing AOAI content filtering, the system includes instructions to detect and prevent harmful content from being included in the response. To validate the effectiveness of the system in detecting harmful content, you need to augment the dataset with the DSB dataset on harmful content adapted for the customer service domain. This enables you to accurately assess error rates and ensure optimal performance. Also, the system is programmed to log any identified harmful content for future analysis. Note: The filter is applied to all domains. Ungrounded content: If an utterance is flagged in production, the administrator reviews it. There are three options available:
In any case, you can use the labeled dataset to evaluate and tune the prompt for harmful content. |
| Prompt injection: A response that requires normalization by GPT may include new instructions that change the intended instructions for GPT. | Reliability and safety |
The system is equipped with instructions to detect prompt injection. To test its robustness in detecting prompt injection, you can augment the dataset with the DSB dataset on prompt injection adapted for the contact center industry. This enables you to accurately measure error rates and guarantee the optimal performance of the system. Additionally, the system is programmed to record any identified harmful content for later examination. Note: The filter is applied to all domains. Similarly to the other harms, if an utterance is flagged in production, the administrator reviews it. There are three options available:
In any case, you can use the labeled dataset to evaluate and tune the prompt for prompt injection. |
What operational factors and settings allow for effective and responsible use of the feature?
Engineers and researchers control operational factors and settings, overseeing various aspects, including the functionality and settings of the system.
The responsibility of the administrator is to validate flagged utterances. Subsequently, based on feedback, engineers and researchers may modify the settings and operational factors of the system.