Architecture
On PSTN-based deployments (NMS), the audio provider and Telephony Session service are responsible for:
- Passing audio between the relevant components. Audio refers to speech acquisition and playback.
- Tone detection and generation.
- Call control. Call control refers to answering incoming calls, transferring calls, and placing outbound calls.
On SIP-based deployments, the audio provider and the Telephony Session service are responsible only for call control. Audio is passed directly between the Nuance Speech Server and gateway. The Speech Server is also responsible for tone detection and generation.
Call flow
Audio is passed using Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP):
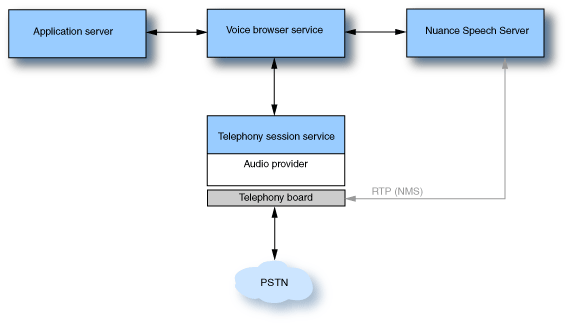
- With the NMS audio provider, audio (RTP) is passed between the Speech Server and the NMS board.
For example:
- With the SIP audio provider, audio (RTP) is passed between the Speech Server and the SIP endpoint like the SIP softphone or gateway. For example:
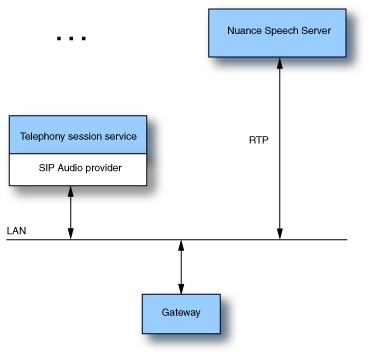
The high-level call flow goes like this:
- A call comes into Voice Platform.
- The audio provider detects the call and notifies the Telephony Session service.
- The Telephony Session service notifies the Voice Browser service.
- The Voice Browser service gets the VoiceXML initial page from the application server and audio resources from the Speech Server.
- The Voice Browser service answers the notification from Telephony Session service.
- The Telephony Session service tells the audio provider to answer the call:
- NMS audio provider: Tells the NMS board to send audio to the Speech Server via RTP.
- SIP audio provider: Tells the SIP endpoint (in this example, the gateway) to send audio to the Speech Server via RTP.
- The Voice Browser service starts executing the VoiceXML application:
- NMS audio provider: The Speech Server transfers audio with the NMS board via RTP.
- SIP audio provider: The Speech Server transfers audio with the gateway via RTP.
For a detailed call flow, see Sequence of events of a call.
Ports specification
Voice Platform components use SIP internally to communicate with each other when processing an inbound call. This illustration shows the default ports, the service properties specified, and services they’re set on. These ports are reserved by Voice Platform regardless of the audio provider you’re using. The one exception is port 5060, set by audio.sip.UserAgentPort on the Telephony Session service. This setting is specific to the SIP audio provider.
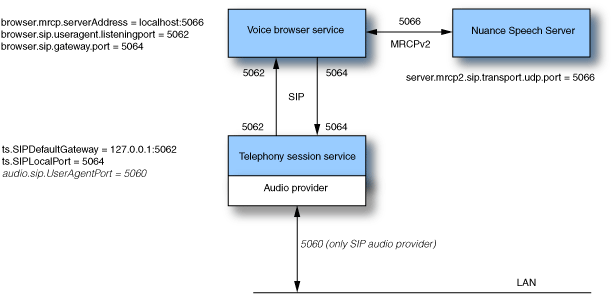
This table provides more information about the ports shown in the illustration. Note that these ports are reserved and should not be used for anything else.
|
Port number |
Description |
|---|---|
|
5060 |
SIP ports used by the SIP audio provider (if specified) to listen for incoming calls. 5060 is reserved for a single service instance. When using multiple instances, the port values increase by 10 for each new instance. |
|
5062 |
SIP ports used by the Voice Browser service to receive SIP messages from the Telephony Session service. 5062 is reserved for a single service instance. When using multiple instances, the port values increase by 10 for each new instance. Note: In the high availability (HA) roles provided by Voice Platform, the defaults for the HA Voice Browser service instances are 6002 (first instance), 6012, 6022, and 6032. |
|
5064 |
SIP ports used by the Telephony Session service to receive SIP messages from the Voice Browser service. 5064 is reserved for a single service instance. When using multiple instances, the port values increase by 10 for each new instance. |
|
5066 |
SIP port used by the Nuance Speech Server for the MRCPv2 connection with the Voice Browser service. 5066 is reserved for a single service instance. When using multiple instances, the port values increase by 10 for each new instance. |
