Bridged transfers
In a bridged transfer, the caller (party A) calls the application, the application connects the caller to the called party (party C) but stays connected to both callers, creating a bridge. The application can also monitor one side of the call.
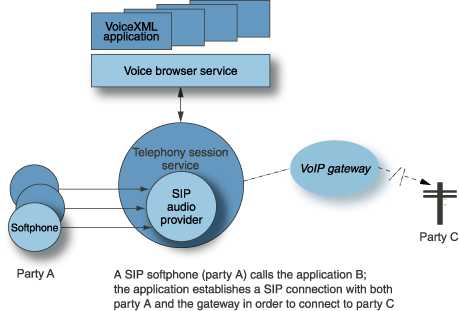
In the following figure, the original call comes in from party A. The SIP audio provider sends an INVITE to the called party, C. Once a response is received from the called party, the audio is streamed between the two parties, and between the application and each party, as shown in the diagram.
Far-end dialog
A far-end dialog specifies a VoiceXML dialog to conduct with the called party before connecting the transfer. It’s enabled with the farenddialog attribute on the <transfer> element.
With far-end dialog: A caller calls the application, the application calls the called party (or far end), and based on interaction (or dialog) with the called party, determines whether or not to connect the user to the far end. If the called party agrees, the application connects the two parties. An example of an application using far-end dialog would be a collect call application.
Without far-end dialog (default): A caller calls the application, the application calls the called party and waits until the called party answers the call before connecting the two parties.
Far-end hot word
A hot word is a specific word or phrase that, once recognized, ends the call to party C and resumes the dialog between party A (caller) and the application. Hot word is set by default on party A. To enable hot word on party C, set the farendhotword attribute to true on the <transfer> element. See <transfer> for more information.
By default, the audio between party A and party C is bridged inside the gateway. While the call is bridged, the Nuance Speech Server doesn’t receive any audio so it can’t perform hot word recognition.
Hot word recognition in a bridged transfer requires that the Telephony Session service fork audio from party A to party C and the Speech Server. See Configuration settings that affect audio routing for more information on how to configure Voice Platform to support audio forking.
